News
First report of cell surface charge mapping with a photoelectrochemical imaging system appears in Analytical Chemistry
15 April 2019
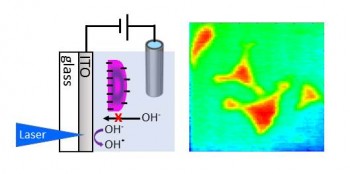
Fan's and Bo's paper on the photoelectrochemical imaging of cell surface charges has been been accepted by Analytical Chemistry. Photoanodic currents at indium tin oxide (ITO) coated glass immersed in an electrolyte solution were shown to be sensitive to surface charge, pH and impedance. Our laser scanning setup allows photoelectrochemical imaging with micron scale resolution. In this work, we cultured different types of cells on the surface of the ITO. The photoanodic current was shown to be dependent on the surface charge of the substrate facing side of cells - an area not accessible to other electrochemical or electrophysiological imaging techniques. The new photoelectrochemical imaging system holds great promise for the investigation of cell responses, cell-surface interactions and cell metabolism.
The details of the paper are as follows:
Fan Wu; Bo Zhou; Jian Wang; Muchun Zhong; Anirban Das; Michael Watkinson; Karin Hing; De-Wen Zhang; Steffi Krause; “Photoelectrochemical imaging system for the mapping of cell surface charges", Analytical Chemistry, doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.9b00304
| Contact: | Steffi Krause |
| Tel: | 020 7882 3747 |
| Email: | s.krause@qmul.ac.uk |
| Website: | |
| People: | Steffi KRAUSE Karin HING |
| Research Centre: | Bioengineering |
Updated by: Steffi Krause




