News
Researchers demonstrate a new method for scalable deposition of hybrid perovskites for solar cells
5 February 2021
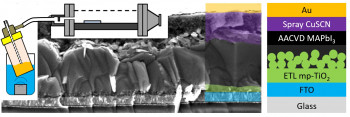
A new paper by Ryley Ratnasingham, supervised by Dr Joe Briscoe (SEMS, QMUL) and Prof Martyn McLachlan (Imperial College London) as part of the Plastic Electronics CDT has been published in Materials Advances, which reports the first ever working perovskite solar cell (PSC) using a hybrid perovskite material deposited by aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposit (AACVD).
PSCs are a new photovoltaic technology that has the potential to lower the cost of solar energy. However, challenges still remain in producing them at large scale and low cost. AACVD is a deposition technique that can deposit functional materials rapidly, over large areas, at low cost. Until now deposition of perovskite material by AACVD has been reported, but not with a uniformity suitable to make a working solar cell. Thus, this paper reports an important first step in successful scale-up of this technology using this technique.
| Contact: | Joe Briscoe |
| Email: | j.briscoe@qmul.ac.uk |
| Website: | |
| People: | Joe BRISCOE Oliver FENWICK |
Updated by: Joe Briscoe




