News
InGaN suitable as a substrate for photoelectrochemical imaging in life sciences
11 October 2019
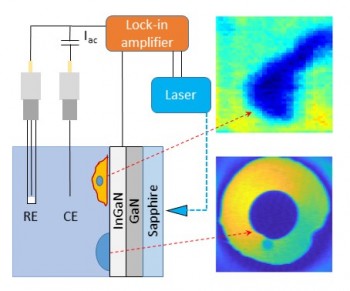
Bo's paper on the use of InGaN as the semiconductor substrate for AC photoelectrochemical imaging has been accepted by Sensors. AC photocurrent imaging at metal oxide semiconductors auch as ITO and ZnO nanorods has been shown to suitable for bioimaging applications such as the measurement of the negative surface charge of isolated cells. However, these substrates require high applied electrical potentials and can only be operated and relatively low frequencies resulting in low imaging speeds. InGaN shows significant photocurrents at low electrical potentials and can be operated at much higher frequencies making this substrate suitable for fast live-cell imaging with a reduced chance of cell damage due to high applied potentials.
The details of the paper are: Bo Zhou, Anirban Das, Menno J. Kappers, Rachel A. Oliver, Colin J. Humphreys
and Steffi Krause; "InGaN as a Substrate for AC Photoelectrochemical Imaging"; Sensors 2019, 19(20), 4386; https://doi.org/10.3390/s19204386
| Contact: | Steffi Krause |
| Tel: | 020 7882 3747 |
| Email: | s.krause@qmul.ac.uk |
| Website: | |
| People: | Steffi KRAUSE Colin HUMPHREYS |
| Research Centre: | Bioengineering |
Updated by: Steffi Krause




