News
Analytical Chemistry paper accepted
22 June 2018
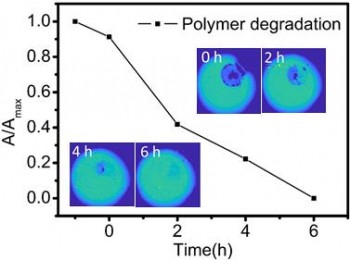
The enzymatic degradation of a polymer was monitored with LAPS images recorded using ZnO nanorods.
Ying's paper on Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors (LAPS) using ZnO Nanorods as the Sensor Substrate for Bioanalytical Applications has been accepted by Analytical Chemistry. In this work, for the first time, a 1D material - ZnO nanorods with a high aspect ratio - was developed as a new substrate material for LAPS imaging. ZnO nanorods showed LAPS photocurrents, which were significantly larger and showed better contrasts than previously observed with ITO. The suitability of the new substrate for sensor and bioimaging applications was demonstrated with its good pH sensitivity without the need for surface modification or a traditional insulator and by monitoring the enzymatic degradation of a polymer film. ZnO nanorods were produced with a simple, inexpensive single step synthesis method. Here are the details of the publication: Ying Tu, Norlaily Ahmad, Joe Briscoe, De-Wen Zhang, and Steffi Krause. Light-Addressable Potentiometric Sensors using ZnO Nanorods as the Sensor Substrate for Bioanalytical Applications. Analytical Chemistry, (2018), DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b02244
| Contact: | Steffi Krause |
| Email: | s.krause@qmul.ac.uk |
| Website: | |
| People: | Steffi KRAUSE |
Updated by: Steffi Krause

