News
Jens Mueller Receives an EC ITN grant
21 May 2012
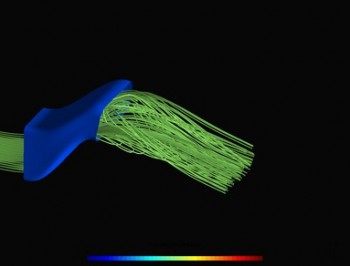
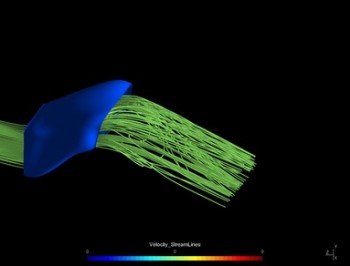
Streamline pattern in S-Bend duct before (a) and after (b) optimisation
Jens Mueller has been successful in securing a 4-year EC ITN project called "About Flow", "Adjoint-based optimisation of industrial and unsteady flows", working with partners including ENGYS UK, Rolls Royce DE and Volkswagen AG. Overall funding is 3-3.5M EUR to the international project consortium. At Queen Mary, 3 PhD studentships and an administrative post are funded.
The results of the project will be applied to realistic mid-size and large-scale industrial optimisation problems ranging from turbo-machinery, to automotive to wind-turbines.
Adjoint-based methods have become the most interesting approach in CFD optimisation due to their low computational cost compared to other approaches. The development of adjoint solvers has seen significant research interest, and a number of EC projects have been funded on adjoint-based optimisation. In particular, partners of this proposal are members of the EC FP7 project FlowHead which develops complete adjoint-based design methods for steady-state flows in automotive design.
Integration of the currently available shape and topology modification approaches with the gradient-based optimisation approach will be addressed, in particular development of interfaces to return the optimised shape into CAD for further design and analysis, an aspect that currently requires manual interpretation by an expert user.
In industrial practice most industrial flows have small levels of instability, which leads to a lack of robustness and instability of the adjoint, such as trailing edge vortex shedding in turbo-machinery. Many industrial applications are also partly unsteady such as bluff body separation in cars or fully unsteady such as vertical-axis wind turbines.
In unsteady adjoints 'checkpoints' of the flow solution at previous timesteps need to be recorded and algorithms for an effective balance between storage and recomputation need to be implemented. The recomputation involves significant memory and runtime overheads for which efficient methods are developed and implemented.
Training will be provided by academic, industrial and SME partners in methods development, industrial application and software management. A large programme of complementary training in professional skills will be provided with support from all partners.
The results of the project will be applied to realistic mid-size and large-scale industrial optimisation problems ranging from turbo-machinery, to automotive to wind-turbines.
Adjoint-based methods have become the most interesting approach in CFD optimisation due to their low computational cost compared to other approaches. The development of adjoint solvers has seen significant research interest, and a number of EC projects have been funded on adjoint-based optimisation. In particular, partners of this proposal are members of the EC FP7 project FlowHead which develops complete adjoint-based design methods for steady-state flows in automotive design.
Integration of the currently available shape and topology modification approaches with the gradient-based optimisation approach will be addressed, in particular development of interfaces to return the optimised shape into CAD for further design and analysis, an aspect that currently requires manual interpretation by an expert user.
In industrial practice most industrial flows have small levels of instability, which leads to a lack of robustness and instability of the adjoint, such as trailing edge vortex shedding in turbo-machinery. Many industrial applications are also partly unsteady such as bluff body separation in cars or fully unsteady such as vertical-axis wind turbines.
In unsteady adjoints 'checkpoints' of the flow solution at previous timesteps need to be recorded and algorithms for an effective balance between storage and recomputation need to be implemented. The recomputation involves significant memory and runtime overheads for which efficient methods are developed and implemented.
Training will be provided by academic, industrial and SME partners in methods development, industrial application and software management. A large programme of complementary training in professional skills will be provided with support from all partners.
| Contact: | Catherine |
Updated by: Catherine Jones




